- PII
- S086960630005671-7-1
- DOI
- 10.31857/S086960630005671-7
- Publication type
- Article
- Status
- Published
- Authors
- Volume/ Edition
- Volume / Issue 3
- Pages
- 62-74
- Abstract
In recent years, owing to comprehensive studies of non-ferrous metallurgy, foundry and jewelry work in Perm Cis-Urals of the Middle Ages, convincing evidence has been obtained for the existence of a large metallurgical centre there that not only provided for the needs of the local population, but also produced commodity metal for exporting. Contrary to the well-established viewpoint that only ore concentrate and copper were supplied there, it was found that local artisans independently doped copper and supplied finished brass and bronze in the form of rod-shaped ingots to the market. The use of Perm cupriferous sandstones for metallurgical production is beyond any doubt. However, the origin of the added metals used in the composition of the alloys remains questionable. Perhaps this issue can be resolved based of the analysis of the morphological and weight characteristics of the master alloy ingots, the preliminary results of which are presented in the article.
- Keywords
- Perm Cis-Urals, the Middle Ages, the Lomovatovka archaeological culture, the Rodanovo archaeological culture, metallurgical centre, non-ferrous metallurgy, alloys, master alloy metal, ingots
- Date of publication
- 23.08.2019
- Year of publication
- 2019
- Number of purchasers
- 89
- Views
- 1048
В эпоху средневековья на территории Восточной Европы широкой популярностью пользовались разнообразные предметы из цветных металлов – украшения и предметы быта, детали вооружения и культовые вещи. Для обеспечения потребностей населения в этих изделиях требовалось большое количество металла, но далеко не во всех областях имелись собственные рудные источники, поэтому приходилось ориентироваться на внешние источники сырья для металлообрабатывающего производства. Очевидно, что торговля металличеcким сырьем имела важное стратегическое значение. Однако в трудах исследователей, занимающихся изучением торгово-экономических вопросов, это направление средневековой торговли обычно не рассматривается, за редким исключением, когда среди экспортируемых и импортируемых товаров указываются слитки цветных металлов (например, Белавин, 2006. С. 327).
В последнее время, после того как Камская археолого-этнографическая экспедиция Пермского государственного гуманитарно-педагогического университета была оснащена прибором для проведения рентгенофлюоресцентного анализа Bruker S1, начались активные исследования химического состава изделий, слитков из цветных металлов, а также плавильных сосудов и литейных форм со следами металла. Результаты этих исследований существенно изменили представления о самом характере литейного производства и о составе используемых сплавов.
Исследование химического состава металла различных изделий из разновременных средневековых памятников Пермского Предуралья показало, что преобладающим сырьем для средневекового литейного производства служили сплавы на основе меди. Часть из них, что характерно в целом для средневековья, соcтавляли многокомпонентные сплавы, являющиеся продуктом многочисленных переплавок вышедших из употребления вещей. Но наряду с этим выделяются достаточно устойчивые составы латуней и бронз, состоящие из 2–4 элементов. Преимущественно с XII в. местными мастерами стали применяться и низкотемпературные сплавы – оловянно-свинцовые, свинцовые или оловянные.
До недавнего времени считалось, что прикамские горняки и металлурги поставляли в Волжскую Булгарию рудный концентрат и товарную медь в виде слитков (Кузьминых, Семыкин, 2006. С. 260), которые отливались в формах-изложницах, найденных на ряде городищ и неукрепленных производственных поселков (Крыласова, 2013. С. 107–110). Далее, уже в мастерских Волжской Булгарии, происходило легирование меди другими металлами (Ениосова и др., 2008. С. 158). Однако обнаружение на средневековых памятниках Пермского Предуралья отдельных оловянных, свинцовых и латунных слитков может свидетельствовать о том, что местные металлурги не только добывали медь из руды, но и самостоятельно проводили ее легирование для получения разных типов сплавов. Возможно, эти сплавы, отлитые в палочковидные слитки в формах-изложницах, не только использовались местными литейщиками, но и поставлялись на экспорт в районы, где отсутствовали собственные разработки цветных металлов. В частности, на территории расселения родственных финно-угорских племен, в Волжскую Булгарию и, вполне вероятно, на территорию Руси. Остановимся на подобных находках подробнее.
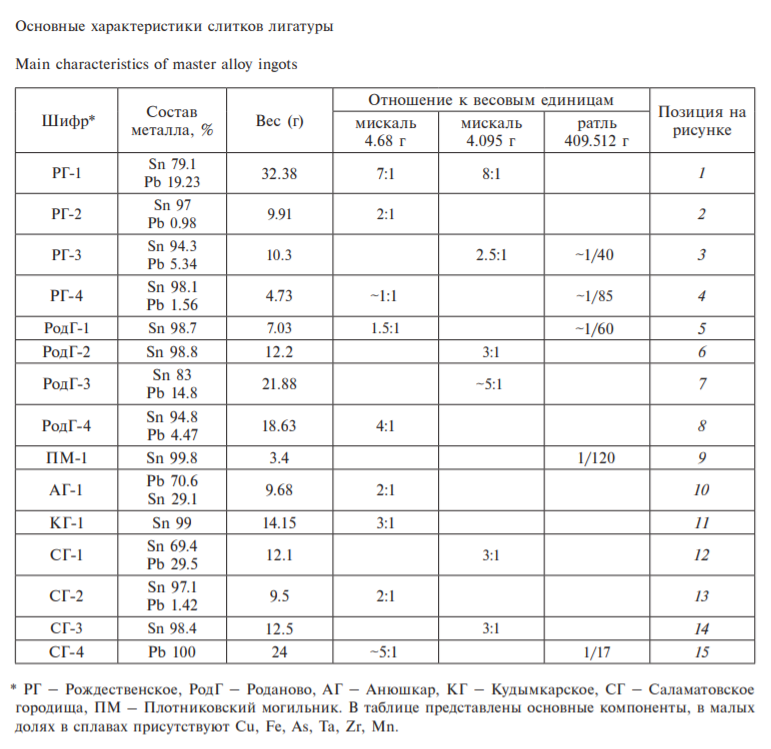
В процессе изучения средневековых коллекций в материалах шести памятников XI–XIV вв. выявлено 1.5 десятка слитков лигатурных металлов (рисунок; таблица). В основном (кроме Плотниковского могильника) слитки происходят с крупных городищ (Рождественское, Роданово, Саламатовское, Анюшкар, Кудымкарское), где изучены металлургические мастерские. Слитки находились преимущественно среди предметов неопределенного назначения и авторами отчетов особо не выделялись.
Химический состав металла слитков исследован (таблица) с помощью портативного рентгенофлюоресцентного анализатора Bruker S1. Один слиток, найденный на Рождественском городище, представлял собой прямоугольный брусок размерами 3 × 2.5, толщиной 0.7 см (рисунок, 1); еще один слиток с этого памятника имел форму вытянутого овала размерами 3.7 × 1.7, толщиной 0.3, с отверстием на одном конце (рисунок, 2).
Все остальные слитки имели форму округлой “лепешки” подпрямоугольного или линзовидного сечения диаметром 2–3.7 см, толщиной 0.2–0.6 см, с отверстием в центре диаметром 0.3–0.8 см (рисунок, 3–15). Слитки отлиты в односторонних открытых формах. Для получения отверстий использовались формы с наличием канала, перпендикулярного литку, куда вставлялся металлический или глиняный стержень. Предположительно такая форма слитков обусловлена тем, что их в определенном количестве (в зависимости от веса) нанизывали на шнур и поставляли связками.
По составу металла слитки можно разделить на следующие группы:
оловянные, с содержанием олова 98.1–99.8% (6 экз., рисунок, 4–6, 9, 11, 14);
оловянные, слегка разбавленные свинцом, с содержанием олова 94.3–97.1% и свинца 0.98–5.34% (4 экз., рисунок, 2, 3, 8, 13);
оловянно-свинцовые, с содержанием олова 69.4–83% и свинца 14.8–29% (3 экз., рисунок, 1, 7, 12);
свинцово-оловянный, с содержанием свинца 70.6% и олова 29.1% (1 экз., рисунок, 10);
свинцовый, с содержанием свинца 100% (1 экз., рисунок, 15).
Наличие свинца в оловянных слитках может объясняться физическими свойствами олова. В чистом виде при температуре ниже 13.2° С этот металл разрушается – трескается и превращается в порошок. Для предотвращения этого разрушения к нему примешивали свинец. Как отмечает С.В. Хаврин, такие свойства белого металла были известны давно, и уже в эпоху средневековья существовали регламенты – сколько примешивать к олову свинца (2011. С. 401). Сохранению слитков с высоким содержанием олова без свинца, вероятнее всего, способствовало наличие в них естественных примесей (Fe, Та, Zr, Mn).
Вес изученных слитков составляет от 3.4 до 32.38 г. Сопоставление с основными весовыми единицами, применявшимися в товарно-денежных отношениях Волжской Булгарии и Урало-Поволжья, показало, что 9 экз. слитков соответствуют 1, 1.5, 2, 3, 5 и 7 мискалям весом 4.68 г; 6 экз. – 2.5, 3, 5 и 8 мискалям весом 4.095 г. В четырех случаях установлено соотношение слитков с иракским ратлем (фунтом) в 409.512 г как 1/40, 1/60, 1/85 и 1/120.
Параллельно с исследованием слитков из легкоплавких металлов проводилась работа по изучению слитков из сплавов на основе меди, которые были продукцией прикамских металлургов и одновременно сырьем для местного литейного производства, где по мере необходимости от них отрубались куски нужного веса. Для всех этих слитков и их обрубков установлена взаимосвязь с древнейшей системой драхмы в 4.26 г, известная в Поволжье с VI в. (Мухаматдиев, 1983. С. 7). По мнению Р.М. Валеева, ранние прикамские бронзовые и латунные слитки были рассчитаны на 25 весовых драхм в 4.26 г (4.26 × 25) = 106 г (1981. С. 87). Как показали исследования, весовые нормы для отливки слитков, основанные на драхме (мискале) в 4.26 г, традиционно сохранялись и в более позднее время. Тот факт, что ни один из оловянных и свинцовых слитков не соотносится с мискалем в 4.26 г, это один из аргументов в пользу предположений об их импортном происхождении.
Поиск аналогий слиткам из легкоплавких металлов затруднителен. Судя по имеющимся публикациям, похожие вещи исследователи чаще всего относят к категориям “грузиков”, “пломб”, “пряслиц”. Обращают на себя внимание так называемые грузики-пломбы, которые десятками встречаются на булгарских поселенческих памятниках. Они имеют определенное сходство с рассматриваемыми слитками по форме (кружок с отверстием) и размерам, но имеют коническую, усеченно-коническую или кружковую форму с цилиндрическим выступом у отверстия (Полякова, 1996. С. 247) и дополнены орнаментом. Об их назначении у исследователей нет единой точки зрения. Преобладает мнение о том, что они использовались в безмонетный период в товарно-денежном обращении.
А.Г. Мухаматдиев приводит такой фрагмент сообщения ал-Гарнати (первая половина XII в.): “У них имеет хождение олово, каждое 8 багдадских маннов стоят динар, разрезают его на куски и покупают на него чего хотят…” (Путешествие…, 1971. С. 58), с которым связывает многочисленные находки “оловянных кружочков с нанесенными на них узорами и дырочкой посередине”. Взвешенные оловянные кружочки в среднем составляли фракции кадака (фунта) в 8, 4 и 2 мискаля по 4.095 г (Мухаматдиев, 1983. С. 26). “Оловянные кружочки с дыркой” рассматривал как один из возможных заменителей денег и Г.А. Федоров-Давыдов (1987. С. 160).
В последующих публикациях данные предметы фигурируют как свинцовые или свинцовооловянные. Упоминаний о том, проводился ли когда-то анализ металла этих изделий, обнаружить не удалось. Возможно, изменение представлений о составе металла связано с версией Р.М. Валеева, также основанной на сообщении ал-Гарнати, о том, что данные кружочки могли являться свинцовыми пломбами, которыми опечатывали связки беличьих шкурок, служивших торговым эквивалентом (например: Валеев, 2007. С. 186), поддержанной многими исследователями.
Подобные “грузики-пломбы” известны и в Пермском Предуралье (Белавин, 2000. С. 126. Рис. 63, 20–23). Результаты исследования химического состава металла таких предметов, найденных при раскопках Роданова городища в 2018 г., показали, что они изготовлены из оловянного сплава (2 экз., где Sn – 97.5 и 98.9%) и оловянного сплава с небольшой примесью свинца (1 экз., Sn – 95.7%, Pb – 2.24%). Один предмет весом 19.23 г соответствует 4 мискалям в 4.68 г, два других весом 11.52 и 21.91 г – 3 и 6 мискалям в 4.095 г. Таким образом, “грузики-пломбы” и по составу металла, и по весовым соотношениям близки рассматриваемым оловянистым слиткам.
С весовой системой, ориентированной на мискаль в 4.095 г, связываются находки свинцово-оловянных слитков на поселениях X–XI вв. в Верхнем Посурье и Примокшанье (Белорыбкин, 2001. С. 65). Причем, как отмечает В.А. Виничек, среди таких слитков преобладали округлые, которые нередко имели в центре сквозное отверстие, необходимое для ношения на шнуре или нити. Только в отличие от анализируемых прикамских слитков, которые отливались сразу с отверстием, в этих слитках отверстия были пробиты острым предметом, похожим на иглу или тонкое шило (Виничек, 2005. С. 122).
Но на территории Волжской Булгарии исследователями подобные слитки не отмечаются. Так, Г.Ф. Полякова, анализируя цветную металлообработку города Болгара, указала на находки нескольких бесформенных слитков и обрубленных кусочков свинца (1996. С. 157). Не исключено, что слитки в виде кружков с отверстием в коллекциях смешаны с упомянутыми деляются. К примеру, в монографии Е.П. Казакова, посвященной сельским поселениям Волжской Булгарии, среди материалов Измерского I селища вместе с типичными “грузиками-пломбами” на иллюстрации представлен предмет, по форме, сечению и отсутствию орнаментации схожий со слитками из Пермского Предуралья (Казаков, 1991. Рис. 19, 21).
В последнее время получены убедительные доказательства того, что одним из важных составляющих элементов экономики Пермского Предуралья было товарное производство металла, в частности сплавов на основе меди, среди которых преобладала свинцовая латунь (Крыласова, 2018. С. 54–69). Однако, что касается источников сырья, только в отношении основного компонента сплавов – меди – нет сомнения в его местном происхождении.
Металлургия меди развивалась в тех горно-металлургических областях, где имелась соответствующая минерально-сырьевая база, включая топливо и флюсы. К таким районам принадлежит таежное Прикамье, на территории которого расположены месторождения медистых песчаников Предуральской рудной провинции и где не было недостатка в древесине для выжига угля (Кузьминых, Семыкин, 2006. С. 258–260). Уже с эпохи бронзы пермские медистые песчаники служили источником для получения меди (Черных, 1970. С. 26–28).
Проявления этой группы медных руд в виде двух полос шириной до 100 км и более тянутся с севера на юг от Верхнекамья до Актюбинска на расстояние более 1500 км. Месторождения в медистых песчаниках располагаются тремя группами. В пределах Пермского края выделяется Верхнекамская или Пермская группа месторождений. Большинство проявлений на территории Пермского края находится в породах шешминского горизонта, протянувшихся полосой шириной 30–70 км через всю территорию края вдоль зоны сочленения Русской плиты с Предуральским краевым прогибом. Песчаники содержат 2–2.5% меди (Минерально-сырьевые ресурсы…, 2006. С. 176, 177). Пермские медистые песчаники относятся к типу убогих окисленных руд, содержание в них меди не отвечает рентабельному минимуму для пирометаллургического процесса. Поэтому после периода их интенсивного использования в древние эпохи и 200-летней промышленной разработки в XVII – начале XIX в. разработка медистых песчаников прекратилась вследствие нерентабельности добычи меди устаревшими методами, вырубки лесов для углежжения, отсутствия дешевой рабочей силы после освобождения крестьян в 1861 г. (Харитонов, 2013).
А.М. Белавиным выделен особый тип средневековых археологических памятников Пермского Предуралья – производственные поселки металлургов, которые концентрировались в районах рудных разработок. Их наличие свидетельствует о том, что уже на ранних стадиях эпохи средневековья возникла хозяйственная специализация и цветная металлургия стала первым производством, в котором начался переход на уровень ремесла (Белавин, Мельничук, 1984. С. 8–16; Белавин, 1987. С. 117–130). В период полевых исследований на подобных памятниках Березниковского археологического микрорайона, расположенных в центре так называемого Кушгортского месторождения медистых песчаников высокого качества, геологи, проводившие разведки на данной территории, сообщили об обнаружении следов более 100 старинных рудников, один из которых в с. М. Романово был осмотрен А.М. Белавиным, но определить время его эксплуатации не представлялось возможным. Основными металлами, использовавшимися для легирования меди, были олово (Sn), свинец (Pb) и цинк (Zn). К наиболее распространенным сплавам, образованным на основе меди с наличием этих элементов, относятся двойная латунь (CuZn), свинцовая латунь (CuZnPb), оловянная (CuSn), свинцовая (CuPb) и свинцовооловянная (CuPbSn) бронзы.
В отличие от меди, которая вне всяких сомнений выплавлялась из местного рудного сырья, происхождение легирующих металлов остается неясным. Попробуем обобщить имеющиеся представления о возможных источниках поступления этих металлов и оценить потенциал местных месторождений.
Олово. Вопросы источников олова как в древности, так и в эпоху средневековья остаются одними из самых неясных в истории металлургии цветных металлов. Основной минерал для получения олова – оловянный камень (касситерит), который химически представляет собой двуокись олова. Получить металлическое олово из оловянного камня не представляет особых трудностей. Для этого его нагревают с древесным углем, при этом начинается восстановление металлического олова, которое в расплавленном состоянии стекает в нижнюю часть печи (Селимханов, 1970. С. 65).
Касситерит и в настоящее время добывается в основном не из коренных пород, а из аллювиальных россыпей – речных наносов. Чем древнее горы, к числу которых принадлежит и Урал, тем больше они подвержены эрозии и тем толще аллювиальные отложения. В связи с этим любопытна и не лишена оснований точка зрения, изложенная в популярной статье В. Тележко: “Древние горы – Урал, Карпаты, Татры, Рудные горы в Центральной Европе – всегда были источником ценных минералов и драгоценных металлов... И если золота, серебра, оловянного камня там сейчас осталось мало, то это не означает, что их никогда там и не было. Они там были, но их не стало в результате интенсивной добычи. Во времена Бронзового века касситерит, медные руды и леса были стратегическими материалами... Отсутствие касситерита в россыпях в тех местах, где процветали цивилизации Бронзового века, означает лишь то, что его вымели там подчистую. И если оловянный камень и сохранился на поверхности в настоящее время, это означает лишь то, что в древности эти места были захолустьем мировой цивилизации” (Тележко, 2015).
Сейчас на территории Пермского края известен всего один рудный объект с содержанием олова 0.02% – это содержание представляет только геохимический интерес и для разработки не пригодно (Минерально-сырьевые ресурсы…, 2006. С. 173). Практическое отсутствие олова в Пермском Предуралье может свидетельствовать и о невозможности его “добычи” в эпоху средневековья. Хотя в археологической литературе можно встретить и противоположную точку зрения. Так, например, А.Л. Хорошкевич писал: “Возможно, в Новгород в небольших количествах попадали цветные металлы из Прикамья. Добыча меди в этом районе достигла высокого уровня. Почти на всех городищах и селищах родановской культуры находят куски руды, литейные формы и различные медные изделия. Часть меди предназначалась, по-видимому, специально для сбыта. Старинные связи Новгорода с этим районом заставляют предполагать, что экспорт меди в Новгород вполне вероятен, однако при отсутствии письменных источников по этой теме вопрос о роли прикамской меди может быть решен только после спектрографических исследований новгородской меди. Так же обстоит дело и с оловом. Олово добывалось в районе Верхней Камы, оттуда попадало и в Прикамье. Достигало ли оно Новгорода, в настоящее время трудно сказать…” (Хорошкевич, 1963. С. 132).
Тем не менее при отсутствии объективных свидетельств существования местной добычи олова следует ориентироваться на внешние источники этого металла. Использование олова как в составе высокотемпературных сплавов, которые существовали начиная с эпохи бронзы и имели широкое распространение в средневековом Прикамье, так и в составе легкоплавких сплавов (свинцово-оловянных), а также в чистом виде в период конца XI – начала XV в., свидетельствует о его регулярных и объемных поставках на территорию Пермского края. Источником поступления олова в эпоху бронзы считаются месторождения оловянной руды (касситерита – SnO2), которые разрабатывались на территории Восточного и Центрального Казахстана, Рудного Алтая, Средней Азии (Куштан, 2011. С. 19). Для более позднего времени предполагаются примерно эти же источники.
Многие исследователи полагают, что олово доставляли с Алтая, где находятся многочисленные россыпи и коренные месторождения. Однако С.В. Кузьминых и Ю.А. Семыкин отмечают, что месторождения олова в Рудном Алтае разрабатывались в эпохи раннего металла и раннего железа, но к III–I вв. до н.э., как свидетельствуют археологические данные, добыча олова здесь прекратилась (2006. С. 262).
Залежи оловянной руды – касситерита и станина – выявлены в Средней Азии на территории Узбекистана, Таджикистана и Афганистана. Свидетельства использования этих рудников относятся к эпохе бронзы, но исключать добычу олова в этом регионе в эпоху средневековья тоже нельзя (Ениосова и др., 2008. С. 158; Garner, 2013. С. 242–245). С.В. Кузьминых и Ю.А. Семыкин отмечают, что именно в средневековье в Средней Азии отмечается резкий подъем добычи полезных ископаемых – олова, свинца, серебра и золота. Поставки этих металлов в Волжскую Булгарию наиболее вероятны именно отсюда, хотя это государство, расположенное на перекрестке торговых путей средневековья, имело налаженные каналы поставки металлов и из других производящих центров (Кузьминых, Семыкин, 2006. С. 262).
В настоящее время большинство разрабатываемых месторождений олова в России находятся на Крайнем Севере и Дальнем Востоке (Развитие…, 2016). О поступлении олова с Дальнего Востока сохранились сведения в письменных источниках. Так, в минералогическом трактате ал-Кашани 1301 г. упомянуто, что Волжская Булгария выступала в качестве основного посредника в торговле оловом между Дальним Востоком и странами Ближнего и Среднего Востока (Ениосова и др., 2008. С. 158). Учитывая тесные торговоэкономические контакты населения Пермского Предуралья с Волжской Булгарией, можно предположить, что олово поступало через ее посредничество.
Свинец и цинк. Т.А. Хлебникова предполагала, что свинцовая и цинковая руда поступала в Волго-Камье с Урала (1996. С. 280). По мнению С.В. Кузьминых и Ю.А. Семыкина, если судить по археологическим и геологическим данным, уральские рудные источники свинца и цинка, доступные для разработки в древности и средневековье, маловероятны (Кузьминых, Семыкин, 2006. С. 262).
В ХХ в. существовало представление, что свинец и цинк очень мало распространены в верхнепермских породах. “Их содержание, за очень редким исключением, не превышает тысячных долей процента… и подавляющее большинство проб с рудных песчаников с территории Пермской области показывает отсутствие данных элементов…” (Нечаев, 1961. С. 453, 454).
В настоящий момент на территории Пермского края известно 18 рудных проявлений свинца. На Панихинском проявлении (Красновишерский р-н) зафиксировано очень высокое содержание свинца (7.7%). Меньшие содержания этого металла (1.0–1.15%) установлены среди известняков на горе Ипат (Красновишерский р-н, Бахаревское проявление). Запасы свинца этого малого месторождения в количестве 91.26 т были даже зафиксированы Уральской территориальной комиссией по запасам полезных ископаемых (Минерально-сырьевые ресурсы…, 2006. С. 173). Эти данные позволяют предполагать, что добыча свинца могла осуществляться непосредственно на территории Пермского Предуралья.
В Пермском крае обнаружено шесть проявлений цинка, максимальное содержание цинка в пробах не превышает 2.18% (Минерально-сырьевые ресурсы…, 2006. С. 173), тем не менее это вполне достаточное содержание для разработки месторождений в средневековую эпоху (если, к примеру, сравнивать с медной рудой).
Свинцесодержащие руды и минералы наиболее распространены на восточном склоне Уральских гор. Уже во второй половине XIX в. в научной геологической литературе появились публикации с описанием не только меднорудных месторождений Среднего и Южного Урала, но и руд, содержащих свинец и цинк.
Н.Г. Меглицкий и А.И. Антипов, проводившие исследования в южной части Уральского хребта в 1854–1855 гг., открыли Преображенский серебро-свинцовый рудник со следами старой выработки. В старых отвалах присутствовала медная минерализация в виде сульфидов и окислов, включая галенит (свинцовый минерал). Химический анализ руд показал наличие 5-6 фунтов свинца и 2.5 золотника серебра в пуде руды (Меглицкий, Антипов, 1858. С. 132–138). А.П. Карпинский выделял для Южного Урала серебросодержащие галенитовые руды в Михайловском и Санарском рудниках Кочкарской площади (1881. С. 27, 28).
Ф.П. Доброхотов отмечал, что свинцовые руды более характерны для восточного склона Уральского хребта, и указывал достаточно много мест, где в заметных количествах встречен галенит (Урал…, 1917. С. 80, 81). Он описывал и цинкосодержащие проявления, указывая, что “цинковые соединения в количестве, достаточном для того, чтобы считать их рудой, до сих пор не были встречены на Урале, но в качестве цинковых минералов известны в нескольких местах Верхотурского уезда” (Урал…, 1917. С. 89), такие представления сформировались уже в XIX в. (Карпинский, 1881. С. 65).
Наиболее богатыми на свинец были Николаевский и Ермаковский свинцовые рудники в Алапаевском р-не с содержанием свинца до 8% (Михеев, 1927). Д.Л. Ортенберг (1927) отмечал наличие галенитовой минерализации в Сапальском руднике недалеко от Нижнего Тагила.
В настоящее время одно из крупнейших производств первичного свинца в России находится в Верхней Пышме (Свердловская обл.). Более 50% свинца, потребляемого на внутреннем рынке, Россия импортирует из Казахстана (Развитие…, 2016), с которым в эпоху средневековья существовали контакты, поэтому нельзя исключать, что часть свинца могла поставляться оттуда. Основным районом выпуска цинковых концентратов является Урал, 55–60% цинка производится на заводе в Челябинске, куда поступают на переработку цинковые концентраты со всего Урала, Северного Кавказа и Сибири. А крупнейшие месторождения цинковых руд в России (40% от российских запасов) находятся на территории Бурятии (Развитие…, 2016).
Таким образом, что касается свинца, то, с одной стороны, есть основания предполагать его местное происхождение, возможно, именно поэтому слитки свинца, по сравнению с оловянными, встречаются значительно реже. С другой стороны, морфологическое сходство свинцовых и оловянных слитков может свидетельствовать о привозном характере и тех, и других. Если слитки олова и свинца импортировались в Прикамье, это, вероятнее всего, осуществлялось через посредничество Волжской Булгарии, с которой существовали тесные экономические, политические и культурные связи.
Цинк в чистом виде ни в виде слитков, ни в виде обрубленных кусочков на средневековых памятниках Пермского Предуралья неизвестен и отмечен пока только в составе искусственных сплавов, как и в Волжской Булгарии (Полякова, 1996. С. 157). Отсутствие слитков цинка объясняется тем, что в чистом виде этот металл стал производиться в достаточно позднее время – в начале XIV в. (по другим данным – с XVI в.) (Хаврин, Чугунова, 2004. С. 351). Латунные сплавы с древнейших времен получали способом цементации. Процесс цементации осуществлялся посредством плавления смеси измельченной меди, оксида цинка и древесного угля при определенных температурных режимах (Ениосова и др., 2000; Егорьков, 2008). Поскольку цинкосодержащие руды известны на территории Пермского края, можно предполагать местное происхождение латунных сплавов (по крайней мере, двойной или свинцовой латуни).
Подводя итог, следует отметить, что торговля металлами, в том числе лигатурами, совершенно напрасно не учитывается в исследованиях, посвященных торгово-экономическим отношениям. Металл как стратегическое сырье, очевидно, занимал в торговле одно из первостепенных мест. Места добычи и производства товарного металла в виде слитков, безусловно, носили характер особых экономических центров, связанных сетью транспортных путей с центрами металлообработки – основными потребителями товарного металла. Одновременно слитки цветного метала, отлитые по определенным весовым нормам, могли выступать в качестве денежного эквивалента, более дешевого, чем серебро, как в период хождения серебряных монет, так и в безмонетный период. Выделение слитков особой характерной формы, определение состава металла, из которого они отлиты, картографирование находок могут способствовать уточнению представлений о системе торговли в Восточной Европе.
Хотелось бы также отметить, что слитки товарного металла, зачастую в обрубках, как правило, содержатся в невыразительной части коллекций археологических памятников среди неопределенных предметов. Возможно, наша попытка охарактеризовать эти предметы позволит исследователям выделить и интерпретировать подобные находки. В связи с этим вызывает серьезные опасения подготовка Министерством культуры России новых, более жестких правил передачи археологических находок музеям, согласно которым археолог должен будет на месте все описать, но в музей передавать только то, что представляет особую ценность. При подобном подходе невыразительные с точки зрения возможного экспонирования материалы, связанные с литейным производством (разнообразный лом, обрубки слитков, полуфабрикаты, не говоря уже о кусках шлака), могут оказаться среди материалов, которые не будут приниматься на хранение. И, таким образом, источник, который с развитием технологий и методов анализа может дать ценную информацию, будет утрачен.
References
- 1. Belavin A.M., 1987. Industrial settlements of the FinnoUgric metallurgists of the late 1st – early 2nd millennium AD. Etnicheskiye i sotsial’nyye protsessy u finno-ugrov Povolzh’ya (I tys. do n.e. – I tys. n.e.) [Ethnic and social processes in the Finno-Ugric population of the Volga region (the 1st millennium BC – the 1st millennium AD)]. Yu.A. Zeleneyev, ed. YoshkarOla: Mar. gos. univ., pp. 117–130. (In Russ.)
- 2. Belavin A.M., 2000. Kamskiy torgovyy put’. Srednevekovoye Predural’ye v ego ekonomicheskikh i etnokul’turnykh svyazyakh [The Kama trade route. Medieval Cis-Urals in its economic and ethnocultural relations]. Perm’: Perm. gos. ped. univ. 200 p.
- 3. Belavin A.M., 2006. The Kama trade route. Istoriya tatar s drevneyshikh vremen [History of the Tatars since ancient times], II: Volzhskaya Bulgariya i Velikaya Step’ [Volga Bulgaria and the Great Steppe]. F.Sh. Khuzin, ed. Kazan’: Rukhiyat, pp. 326–330. (In Russ.)
- 4. Belavin A.M., Mel’nichuk A.F., 1984. Medieval sites near the village of Volodin Kamen in the estuary region of the river Yayva. Pamyatniki zheleznogo veka KamskoVyatskogo mezhdurech’ya [The Iron Age sites of the Kama-Vyatka interfluve], 2. B.G. Plyushchevskiy, ed. Izhevsk: Udm. gos. univ., pp. 8–16. (In Russ.)
- 5. Belorybkin G.N., 2001. Zolotarevskoye poseleniye [Zolotarevka settlement]. St. Petersburg: IIMK RAN. 198 p.
- 6. Chernykh E.N., 1970. Drevneyshaya metallurgiya Urala i Povolzh’ya [The earliest metallurgy of the Urals and the Volga region]. Moscow: Nauka. 180 p. (MIA, 172).
- 7. Egor’kov A.N., 2008. Bronze and brass production by cementation in antiquity. Arkheologicheskiye vesti [Archaeological news], 15. E.N. Nosov, ed. Moscow: Nauka, pp. 157–162. (In Russ.)
- 8. Eniosova N.V., Mitoyan R.A., Saracheva T.G., 2000. Brass from medieval Novgorod. Novgorod i Novgorodskaya zemlya. Istoriya i arkheologiya [Novgorod and the Novgorod land. History and archaeology], 14. P.G. Gaydukov, comp. Velikiy Novgorod: Novg. gos. ob”yed. muzey-zapovednik, pp. 99–111. (In Russ.)
- 9. Eniosova N.V., Mitoyan R.A., Saracheva T.G., 2008. The chemical composition of raw jewelry materials of the Middle Ages and routes of their import to Rus. Tsvetnyye i dragotsennyye metally i ikh splavy na territorii Vostochnoy Evropy v epokhu srednevekov’ya [Non-ferrous and precious metals and their alloys in Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages]. Moscow: Vost. lit., pp. 107–189. (In Russ.)
- 10. Fedorov-Davydov G.A., 1987. Money coining and circulation of Bolghar. Gorod Bolgar. Ocherki istorii i kul’tury [The town of Bolghar. Studies on history and culture]. G.A. Fedorov-Davydov, ed. Moscow: Nauka, pp. 158–204. (In Russ.)
- 11. Garner J., 2013. Das Zinn der Bronzezeitin Mittelasien. Die montanarchäologischen Forschungen an den Zinnlagerstätten. Darmstadt: Von Zabern. 483 p. (Archäologie in Iran und Turan).
- 12. Karpinskiy A.P., 1881. Mineral deposits in the Urals. Ocherk mestorozhdeniy poleznykh iskopayemykh v Evropeyskoy Rossii i na Urale [A study on mineral deposits in European Russia and in the Urals]. St. Petersburg: Tip. V. Demakova, pp. 3–86. (In Russ.)
- 13. Kazakov E.P., 1991. Bulgarskoye selo X–XIII vekov nizoviy Kamy [Bulgar village of the 10th–13th centuries in the lower Kama region]. Kazan’: Tat. knish. izd. 176 p.
- 14. Kharitonov T.V. Permskaya med’ i eye istoriya (Elektronnyy resurs) [Perm copper and its history (Electronic resource)]. URL: https://uraloved.ru/geologiya/uralskaya-med/istoriya-permskoy-medi.
- 15. Khavrin S.V., 2011. Archaeological tin. Trudy III (XIX) Vseros. arkheol. s”yezda [Proceedings of the III (XIX) All-Russian Archaeological Congress], I. N.A. Makarov, E.N. Nosov, eds. St. Petersburg; Moscow; Velikiy Novgorod: Novgor. tekhnopark, p. 401. (In Russ.)
- 16. Khavrin S.V., Chugunova K.S., 2004. Ancient brass: issues of origin, spreading and interpretation. Kompleksnyye issledovaniya drevnikh i traditsionnykh obshchestv Evrazii [Comprehensive studies of ancient and traditional societies of Eurasia]. Yu.F. Kiryushin, A.A. Tishkin, eds. Barnaul: Izd. Alt. univ., p. 351. (In Russ.)
- 17. Khlebnikova T.A., 1996. Analyses of the Bulgar nonferrous metal. Gorod Bolgar: Remeslo metallurgov, kuznetsov, liteyshchikov [The town of Bolghar: Craft of metallurgists, blacksmiths, and foundrymen]. G.A. Fedorov-Davydov, ed. Kazan’: Institut yazyka, literatury i iskusstva, pp. 269–292. (In Russ.)
- 18. Khoroshkevich A.L., 1963. Torgovlya Velikogo Novgoroda s Pribaltikoy i Zapadnoy Evropoy v XIV– XV vv. [The trade of Veliky Novgorod with the Baltic states and Western Europe in the 14th–15th centuries]. Moscow: Izd. AN SSSR. 368 p.
- 19. Krylasova N.B., 2013. Casting mould risers: to the issue of commodity production of copper and its alloys in Perm Cis-Urals. Perekhodnyye epokhi v arkheologii: materialy konferentsii “XIX Ural’skoye arkheologicheskoye soveshchaniye” [Transitional periods in archaeology: Proceedings of the conference “XIX Ural Archaeological Meeting”]. I.O. Vaskul, ed. Syktyvkar: Komi NTs UrO RAN, pp. 107–110. (In Russ.)
- 20. Krylasova N.B., 2018. To the development of A.M. Belavin’s concept on the commodity production of copper and copper-based alloys in the medieval Perm Cis-Urals. Srednevekovaya arkheologiya Evrazii: ot Yamala do Karpat. K 60-letnemu yubileyu A.M. Belavina [Medieval archaeology of Eurasia: from Yamal to the Carpathians. To the 60th anniv. of A.M. Belavin]. N.B. Krylasova, ed. Perm’: Perm. gos. gum.-ped. univ., pp. 54–69. (Trudy Kamskoy arkheologo-etnograf. ekspeditsii, XIV). (In Russ.)
- 21. Kushtan D.P., 2011. The Trans-Eurasian “tin” route of the late Bronze Age. Perekhod ot epokhi bronzy k epokhe zheleza v severnoy Evrazii: materialy kruglogo stola [Transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age in Northern Eurasia: Proceedings of the round table]. V.A. Alekshin, V.S. Bochkarev, eds. St. Petersburg: IIMK RAN, pp. 19–21. (In Russ.)
- 22. Kuz’minykh S.V., Semykin Yu.A., 2006. Non-ferrous metal working. Istoriya tatar s drevneyshikh vremen [History of the Tatars since ancient times], II: Volzhskaya Bulgariya i Velikaya Step’ [Volga Bulgaria and the Great Steppe]. F.Sh. Khuzin. Kazan’: Rukhiyat, pp. 258–272. (In Russ.)
- 23. Meglitskiy N.G., Antipov A.P., 1858. Geognosticheskoye opisaniye yuzhnoy chasti Ural’skogo khrebta, issledovannoy v techeniye 1854 i 1855 gg. [Geognostic description of the southern part of the Ural range explored in 1854 and 1855]. St. Petersburg: Tip. Dep. vneshney torgovli. 435 p.
- 24. Mikheyev N.S., 1927. Nikolaevsky and Ermakovsky lead mines in the Urals. Mineral’noye syr’ye [Mineral raw materials], 7–8, pp. 428–431. (In Russ.)
- 25. Mineral’no-syr’yevyye resursy Permskogo kraya: entsiklopediya [Mineral and raw resources of Perm Territory: Encyclopaedia]. A.I. Kudryashov, ed. Perm’: Gornyy inst. UrO RAN, 2006. 458 p.
- 26. Mukhamatdiyev A.G., 1983. Bulgaro-tatarskaya monetnaya sistema XII–XV vv. [Bulgaro-Tatar monetary system of the 12th–15th centuries]. Moscow: Nauka. 188 p.
- 27. Nechayev Yu.A., 1961. Lead and zinc in the copper sandstones of Perm Region. Geokhimiya [Geochemistry], 5, pp. 453–454. (In Russ.)
- 28. Ortenberg D.L., 1927. Ores of the lower horizons of Sapalsky manganese mine. Mineral’noye syr’ye [Mineral raw materials], 3, pp. 163–176. (In Russ.)
- 29. Polyakova G.F., 1996. Objects from non-ferrous and precious metals. Gorod Bolgar: Remeslo metallurgov, kuznetsov, liteyshchikov [The town of Bolghar: Craft of metallurgists, blacksmiths, and foundrymen]. G.A. Fedorov-Davydov, ed. Kazan’: Institut yazyka, literatury i iskusstva, pp. 154–258. (In Russ.)
- 30. Puteshestviye Abu Khamida al-Garnati v Vostochnuyu i Tsentral’nuyu Evropu (1131–1153 gg.) [The journey of Abu Hamid al-Garnati to Eastern and Central Europe (1131–1153)]. O.G. Bol’shakov, A.L. Mongayt, eds. Moscow: Vost. lit., 1971. 134 p.
- 31. Razvitiye i razmeshcheniye tsvetnoy metallurgii (Elektronnyy resurs) [Development and location of non-ferrous metallurgy (Electronic resource)]. URL: http://poznayka.org/s3760t.html.
- 32. Selimkhanov I.R., 1970. Razgadannyye sekrety drevney bronzy [Unraveled secrets of ancient bronze]. Moscow: Nauka. 82 p.
- 33. Telezhko V. Bronzovyy vek, olovo i nisprovergateli istorii (Elektronnyy resurs) [The Bronze Age, tin and history subverters (Electronic resource)]. URL: http://www.proza.ru/2015/09/22/1405.
- 34. Ural Severnyy, Sredniy, Yuzhnyy: Spravochnaya kniga [The North, Middle, South Urals: a reference book]. F.P. Dobrokhotov, V.A. Vesnovskiy, V.S. Zybin, comp. Petrograd: Izd. V.A. Suvorina, 1917. 811 p.
- 35. Valeyev R.M., 1981. To the issue of commodity-money relations of the early Bulgars (the 8th–10th centuries). Iz istorii rannikh bulgar [From the history of the early Bulgars]. A.Kh. Khalikov, ed. Kazan’: IIYaLI, pp. 83–96. (In Russ.)
- 36. Valeyev R.M., 2007. Torgovlya i torgovyye puti Srednego Povolzh’ya i Priural’ya v epokhu srednevekov’ya (IX – nachalo XV v.) [The trade and trade routes of the Middle Volga and Cis-Ural regions in the Middle Ages (the 9th–early 15th century)]. Kazan’: Izd. Kazan. univ. 392 p.
- 37. Vinichek V.A., 2005. Remeslo i torgovlya v Verkhnem Posur’ye v XI – nachale XIII v.: dis. … kand. Istorich. nauk [The craft and trade in the Upper Sura region in the 11th–early 13th century: a thesis for a Doctoral degree in History]. Penza. 212 p. (Unpublished)